Glossary
We are dedicated to answering the questions you may have. Have an AAC or AT acronym, concept, or term you would like us to explain? Send us a request!
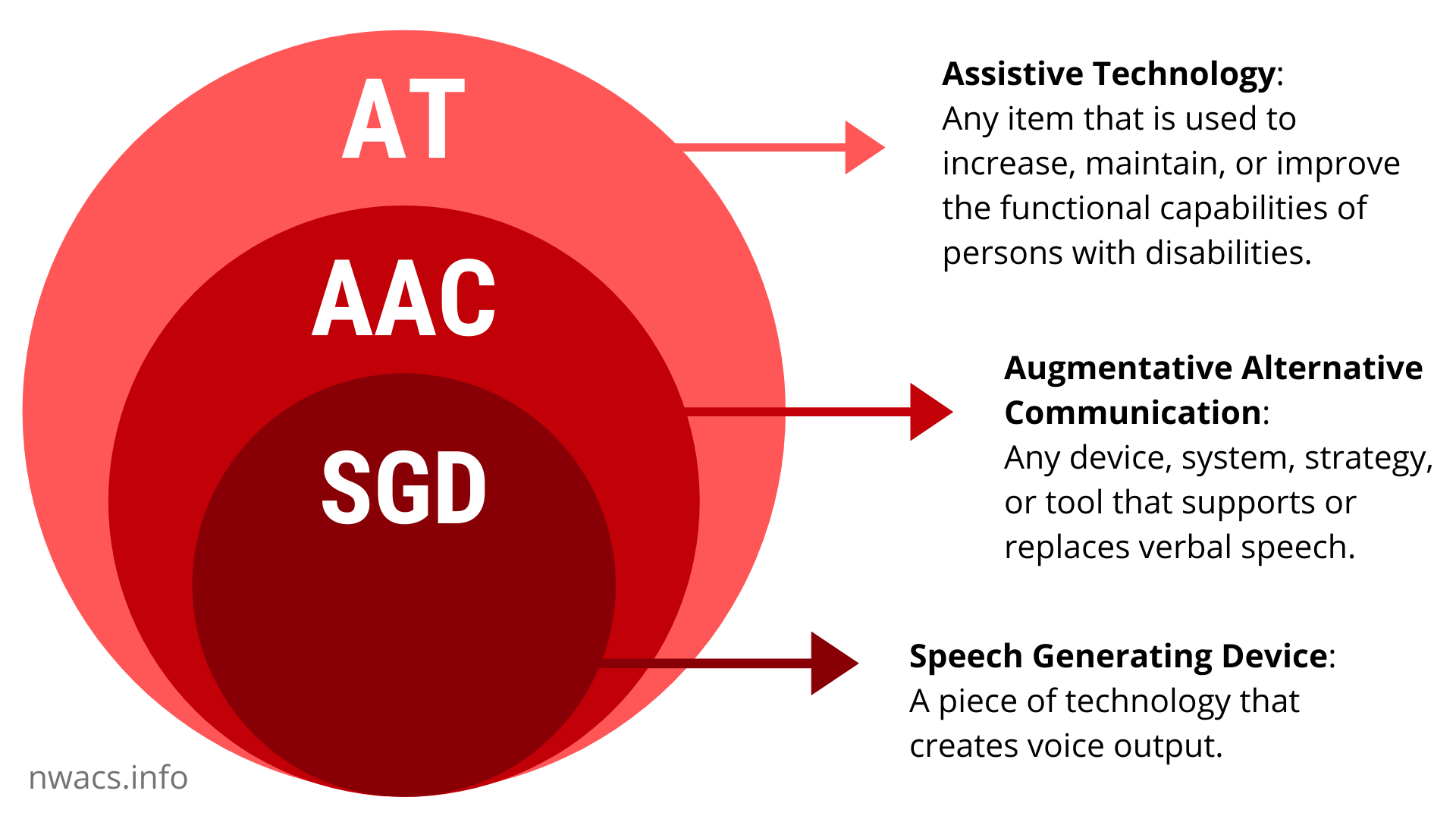
AAC
AAC means Augmentative and Alternative Communication. AAC is anything other than speech that a person uses to help them meet their communication needs. Learn more about Types of AAC.
AAC Abandonment
AAC abandonment is when a person stops using their AAC device even when it is still needed and in working order.
Aided Language Input
Aided language input, or modeling, refers to communication partners using the AAC system to communicate with and around the AAC learner. The goal is to immerse the AAC learner in their AAC language.
AT
AT means Assistive Technology. AT is any product, equipment, or system that enhances learning, working, and daily living for people with disabilities.
Attributing Meaning
Attributing meaning is an important communication partner strategy. It means
identifying communication acts, such as
body movements (reaching for, pushing away, looking at, turning away, etc.)
facial expressions
vocalizations
activations on an AAC system
making a smart guess at what the person may be trying to communicate with that communication act, taking into account the context/situation and what we know about the person
responding to the intent being communicated by all communication acts; this can include
describing the behavior you are identifying as a communication act (“I see you smiling!”)
state what you think it means (“I think you like that!”)
model a way to express that meaning using AAC (LIKE)
honor their communication or otherwise respond to their communication act
Autonomous Communication
Autonomous communication is being able to communicate your own authentic messages and intentions. Communication autonomy is not related to the person’s ability to independently operate their AAC system. It does mean that the person is able to say whatever they want (to whoever they want, in the time and place of their choosing).
CCN
CCN means complex communication needs. People with complex communication needs are not able to meet their communication needs by using verbal speech (mouth words).
Communication Bill of Rights
The Communication Bill of Rights is a list of 15 basic communication rights of all people. Read more about the Communication Bill of Rights.
Communication Functions
Communication functions are all the different reasons that we communicate. We communicate to get our wants and needs met. We also communicate to inform, persuade, and motivate. For social connectedness. And so much more! Read more about communicative functions.
Communication partners are all of the people around the AAC user.
Communication Partners
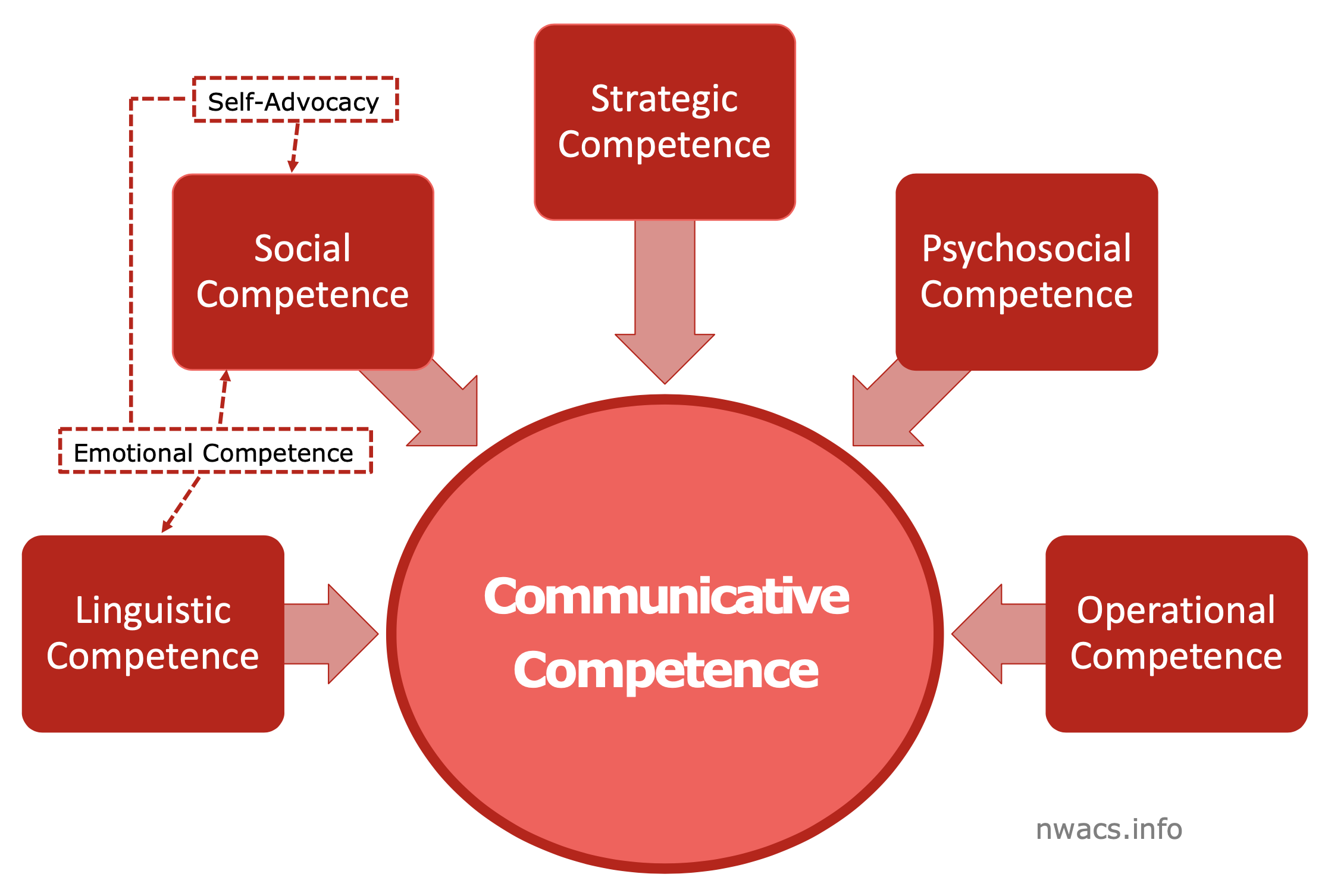
Communicative Competence
Communicative competence is a group of skills that let a person communicate about anything to anyone. This includes skills in the areas of
linguistic,
operational,
social,
strategic,
psychosocial,
emotional,
and self-advocacy,
as well as a supportive environment.
Learn more about communicative competence in our blog series.
Context-Dependent Communicator
A context-dependent communicator is a person of any age who has reliable symbolic communication, but is limited to specific contexts or communication partners. Read more about communication abilities levels.
Conventional methods
Conventional methods of communication are ways of communicating that are commonly used by the larger community. The meaning is obvious and clear to communication partners (receivers). Conventional methods of communication are usually symbolic (can also include common gestures and facial expressions).
Core Words/ Vocabulary
Core words are a set of 300-400 words that make up about 80% of what we say. Core words are mostly verbs, pronouns, adjectives, prepositions, and other words that carry a lot of meaning. Core words are flexible. They can be used across contexts, activities, and environments. Read more about core words.
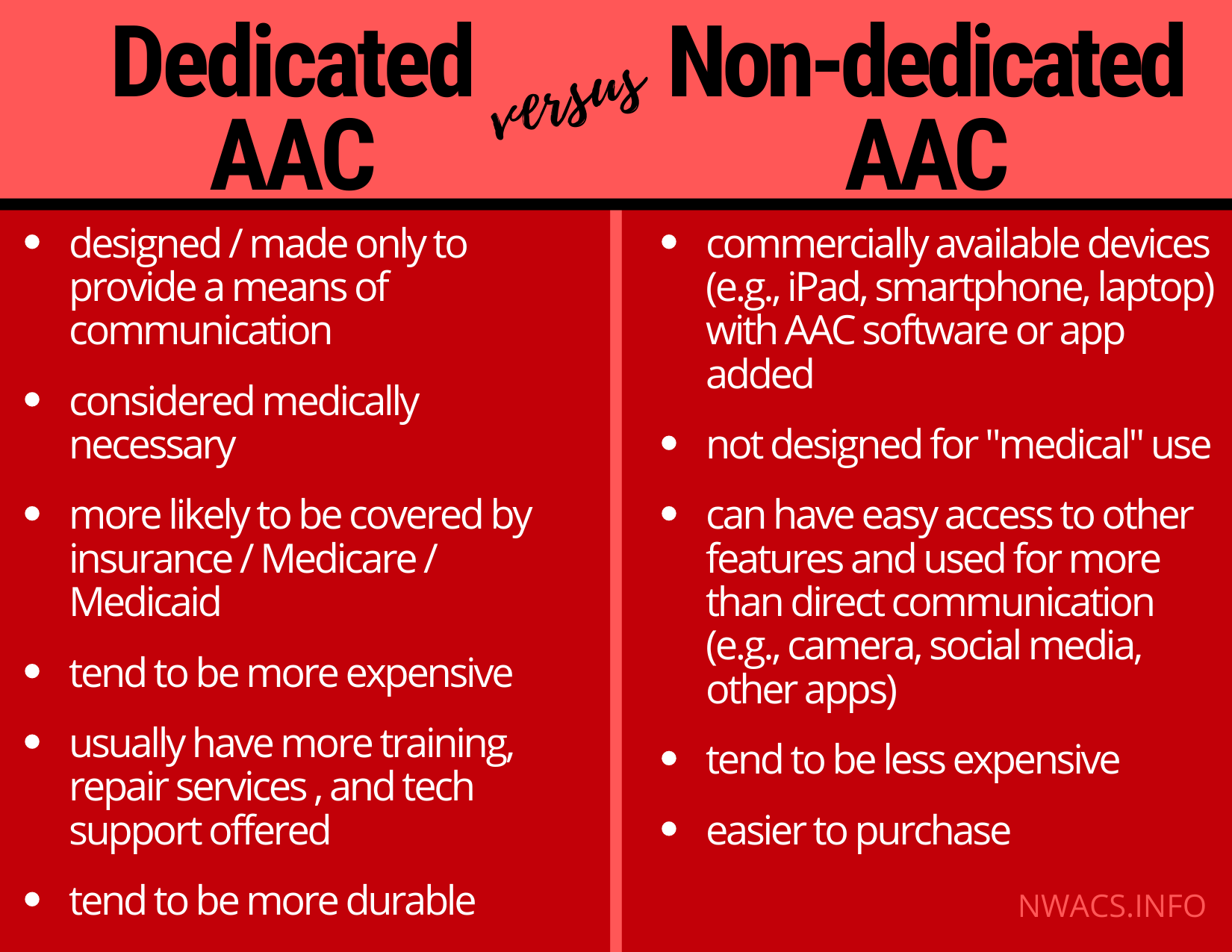
Dedicated Device
A “dedicated device” is an AAC tool designed and made by a specialized company to give people who need AAC a way to communicate. Non-dedicated devices are electronic devices you can buy “off the shelf” and add software or apps to so they function as AAC systems. Learn more HERE
Dynamic Communication System
Dynamic communication systems are a type of high-tech AAC. The display of the system changes or opens to new pages when buttons are pressed.
Emergent Communicator
An emergent (or emerging) communicator is a person of any age who does not have a reliable means of expressive communication using symbolic communication. Read more about communication abilities levels.
Feature matching in AAC is the process of:
first determining what features an AAC user needs in a communication system
and then finding tools and strategies that have those features to trial.
Feature Matching
Fringe Words/ Vocabulary
Fringe words are low frequency words that are specific to a person, place, topic, or activity. Fringe words are typically nouns (names of people, places, things) and make up only 20-25% of what we say. These words are restrictive and only useful when we are talking about the particular topic or things.
IDD
IDD means Intellectual and/or Developmental Disabilities. These are disabilities that are usually present at birth, but may start sometime during childhood, and affect the person’s physical, intellectual, and/or emotional development.
Independent Communicator
An independent communicator is a person who can communicate when, where, why, and to whom they want about anything they want. Read more about communication abilities levels.
Modeling
Modeling, or aided language input, refers to communication partners using the AAC system to communicate with and around the AAC learner. The goal is to immerse the AAC learner in their AAC language.
Motor Planning
Motor planning is a skill that helps us remember and do the steps in the right order to make a movement happen. Over time it allows a person to automatically do something without a lot of thinking to figure out how. In AAC it often refers to having words always in the same place so the AAC user can use a consistent motor plan to say those words.
Multimodal Communication
Multimodal communication is when a person can communicate in a variety of different ways. For example, a person communicating by using a combination of:
body language
vocalizations and/or speech
gestures and/or signs
light-tech AAC
high-tech AAC
spelling
Non-symbolic Communication
Communication that does not use symbols (e.g., sign language, spoken/written words, pictures, symbols). Non-symbolic communication includes using: gestures, vocalizations (sounds), intonation, facial expressions, body movements, proximity, eye gaze, and “behaviors”. It can range from unconventional to conventional.
OT
OT means Occupational Therapist or occupational therapy.
One-hit Speech Output Device
One-hit speech output devices are communication tools activated by a single press. They are also called single message communication devices. These are usually battery-operated devices. A message can be voice recorded on it. The recorded message can be played back by activating the device. A BIGmack is an example. Or explore our Light- & Mid-Tech resource for a list of companies offering various "one-hit speech output" devices.
Partner-Assisted Scanning
The communication partner gives options by showing and/or speaking items. The communicator makes selections by indicating “yes” or “no”. For more information, watch this video from Cincinnati Children’s.
Personal Core/ Vocabulary
Personal core are fringe words are that really important to and more frequently used by a person. These might be words important in the person’s culture or family, related to medical and or sensory needs of the person, special interests of the person, names of people in the person’s life, etc.
PT
PT means Physical Therapist or physical therapy.
SGD or Speech Generating Device
SGD means Speech Generating Device. SGDs are specially made devices for helping people communicate by speaking messages out loud.
Single Message Communication Device
Single message communication devices are communication tools activated by a single press. These are usually battery-operated devices. A message can be voice recorded on it. The recorded message can be played back by activating the device. A BIGmack is an example. Or explore our Light- & Mid-Tech resource for a list of companies offering various "one-hit speech output" devices.
SLP
SLP means Speech Language Pathologist.
Smart Partner
Smart communication partners share the responsibility with the AAC user for successful interactions. They use a variety of strategies to support the person to communicate autonomous messages.
SNUG
SNUG means spontaneous novel utterance generation. SNUG means having the ability (and access to words) to combine words in the way you want to say anything you want. Read more HERE
Static Communication System
Static communication systems are a type of AAC with a single page or screen only. The display of the system does not change or open to new pages when buttons are pressed.
Symbolic Communication
Communication using symbols that have a shared meaning between the sender and the receiver. Symbols include: sign language, spoken/written words, pictures, symbols, and objects.
Text-to-speech (TTS)
Text-to-speech is a type of assistive technology that reads the text on a screen out loud.
Unconventional methods
Unconventional methods of communication are ways of communicating not commonly used by the larger community. The meaning is less obvious and is often unique to the communicator (sender). Unconventional methods of communication tend to be non-symbolic.
Verbal Referencing
Verbal referencing is a supportive teaching technique. The communication partner describes what the person is doing. Then they explain what they think that action means. For example, “I see you turning your head away. I think that means you do not want a drink.”
Visual Supports
A visual support is an item, such as
an object
a photograph, symbol, or drawing
a graphic
something written
that helps a person understand and/or remember. We all use visual supports. Think about your calendar, planner, sticky note reminders, and to-do lists!
VOCA
VOCA means Voice Output Communication Aid. VOCAs are like SGDs. The speech output is either:
digitized (recorded) speech or
synthesized (computer generated/artificial)